Type 1 Diabetes
In the past, patients with Type 1 Diabetes traditionally had two treatment options: take regular doses of insulin, or control their blood sugar with diet and exercise. There may be an alternative method for managing the symptoms. Please fill out a medical review form, or contact our office in Glenview, Illinois at (844) 446 7827 to learn more.
Get an Appointment
Complete The Form Below And We’ll Get Back To You Immediately.
In the past, patients with Type 1 Diabetes traditionally had two treatment options: take regular doses of insulin, or control their blood sugar with diet and exercise. There may be an alternative method for managing the symptoms. Please fill out a medical review form, or contact our office in Glenview, Illinois at (844) 446 7827 to learn more.
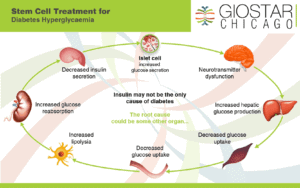
What is Diabetes?
When you consume carbohydrates, they’re digested into glucose, which every cell in your body uses to produce energy. After glucose enters your bloodstream, insulin moves it out of your blood and into cells.
When you don’t have enough insulin, or your body can’t use the insulin that’s available, blood sugar increases beyond a healthy level. This results in a condition called diabetes.

Get an Appointment
Complete The Form Below And We’ll Get Back To You Immediately.
What is Type 1 Diabetes?
Type 1 Diabetes is an autoimmune disease, in which your immune system attacks cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. This shortage of insulin causes blood glucose to rise to unhealthy levels.
Patients with Type 1 Diabetes develop symptoms such as:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Bedwetting
- Extreme hunger
- Unintended weight loss
- Irritability and mood swings
- Fatigue and weakness
- Blurred vision
Although Type 1 Diabetes can occur at any age, it’s most often diagnosed during adolescence and early adulthood, with 85% of all cases appearing before the age of 20.
What Are the Long-Term Consequences of Traditional Treatments?
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus – once known as “juvenile diabetes” or “insulin-dependent diabetes” – is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin. This results in high blood sugar levels in the body. Patients with Type 1 Diabetes always need to use insulin to control their blood sugar. With children and adolescents, it is a very challenging condition to manage insulin, carbohydrate intake, and physical activities on a daily basis. Hypoglycemia is a common occurrence and requires immediate attention.
Long-term complications can occur at a relatively young age, and it is a disease which requires a great deal of emotional support. To understand the daily grind of counting carbohydrates, testing blood sugars multiple times each day, and dealing with the highs and lows (both physical and emotionally) can be very challenging for the patient and family.
Some long-term complications of Type 1 Diabetes that can develop over a span of 10 years are:
- Kidney Disease (Diabetic nephropathy including dialysis and kidney transplant)
- Nerve Disease (Diabetic neuropathy)
- Loss of Vision (Retinopathy)
- Heart Dysfunction (affects the large blood vessels, causing plaque to eventually build up and potentially leading to a heart attack)
- Peripheral Neuropathies (a sore that can get infected in the foot)
- Premature Demise
What is the Possible Role of Stem Cells?
Within the body, there are different sources of stem cells – known as the “mother” or “master” cells – capable of differentiating into virtually any type of cell. It has been documented by several scientific publications that stem cells may differentiate into a specific cell or tissue type.